Autonomous Scientific Discovery Survey Analysis
SPECIAL REPORT: "From AI for Science to Agentic Science"
Key Digest and Analysis of the Latest Paradigm Shift in Scientific AI
The Core Concept: Defining Agentic Science
**Agentic Science** marks the transition of AI from a specialized tool to an autonomous scientific partner. It represents a pivotal stage where AI systems can independently execute the entire scientific discovery cycle, encompassing **novel hypothesis formulation, experimental design, execution, interpretation, and iterative refinement**—all with minimal human guidance.
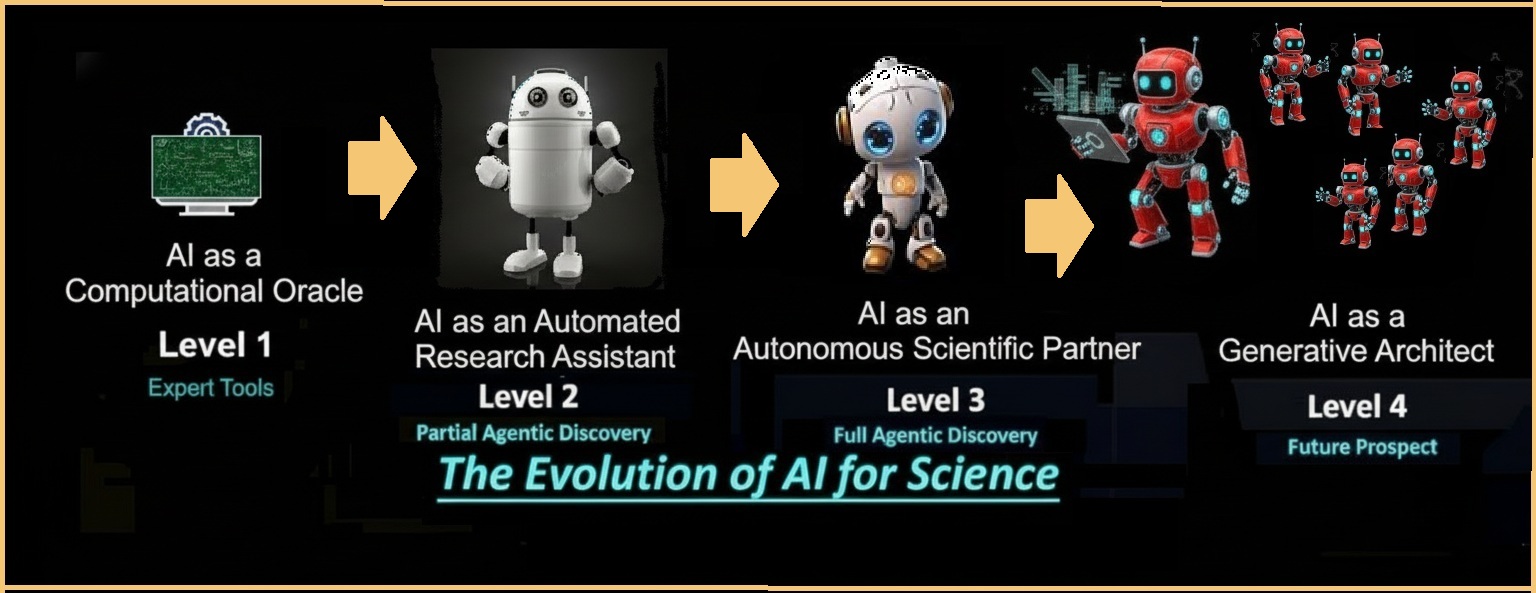
The Four Levels of Scientific AI Evolution
The survey charts the evolution of AI's role through four distinct levels of increasing autonomy:
Level 1: Computational Oracle (Expert Tools)
Autonomy: None
AI models are highly specialized, solving discrete problems. Requires **constant human guidance** for task definition and execution.
Level 2: Automated Research Assistant
Autonomy: Partial
AI automates **specific, pre-defined stages** of research (e.g., data analysis pipeline). High-level scientific direction is still provided by the human.
Level 3: Autonomous Scientific Partner (Agentic Science)
Autonomy: Full
AI conducts the **entire scientific discovery cycle independently**, moving from observation and hypothesis to iterative refinement.
Level 4: Generative Architect (Future Prospect)
Autonomy: Tool-Creator
The ultimate stage where AI invents **new scientific instruments, conceptual frameworks, or methodologies**.
The Dynamic Discovery Workflow
The agent-driven process is a continuous, iterative loop focused on self-improvement:
Observation & Hypothesis Generation
The agent identifies knowledge gaps and formulates a novel, testable theory.
Experimental Planning & Execution
Designing a precise experiment and carrying it out, often by controlling physical or virtual lab equipment.
Data and Result Analysis
Interpreting raw data, transforming it into insights, and drawing conclusions about the initial hypothesis.
Synthesis, Validation, & Evolution
The agent evaluates its findings, validates the discovery, and uses the new knowledge to **refine its internal model** for the next cycle.
Key Challenges and the Human Role
Major Hurdles to Overcome
- **Transparency in Reasoning:** Addressing the "black box" nature of LLMs to ensure that the agent's scientific conclusions are fully **auditable and reproducible**.
- **Ethical and Societal Dimensions:** Establishing clear **accountability** for autonomous findings and mitigating the risks associated with **dual-use outcomes** (e.g., discovery of hazardous materials).
- **Reproducibility & Validation:** Ensuring that AI-generated discoveries are not only novel but also robust and can be verified by the broader scientific community.
The Evolving Role of the Scientist
The human role shifts from **executor** to **strategist and validator**:
- ● Setting broad, ethical research goals.
- ● Mastering **agent prompting** (clear, context-rich instructions).
- ● Scrutinizing the agent's outputs for scientific trust and validity.
The Ultimate Benchmark: The Nobel-Turing Test
The field's maturity will be proven when an autonomous agent makes a foundational scientific discovery worthy of a Nobel Prize, requiring non-obvious, novel experimental methodology.